[powerkit_collapsible title=”Not using Ubuntu? Choose a different version or distro.”]
Debian 10/11
[/powerkit_collapsible]
Oracle VM VirtualBox is a proprietary, cross-platform virtualization software that let you run multiple guest operating systems on your present operating system (called guest OS), under the same hardware.
VirtualBox is straightforward to use. You need to do a few steps to get a running guest operating system. There are also some advanced virtualization options that expert users can tweak to get the best performance.
This article will show how to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu. There are three methods to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu.
Table of Contents
VirtualBox Graphical Installation
We are going to download VirtualBox from its website, so you have to follow a straightforward set of steps. The good thing is you are going to install the latest version in an easy way, but the downside that you have to do these steps every time a new release is out.
Open a browser. Here we’ll be using Firefox.
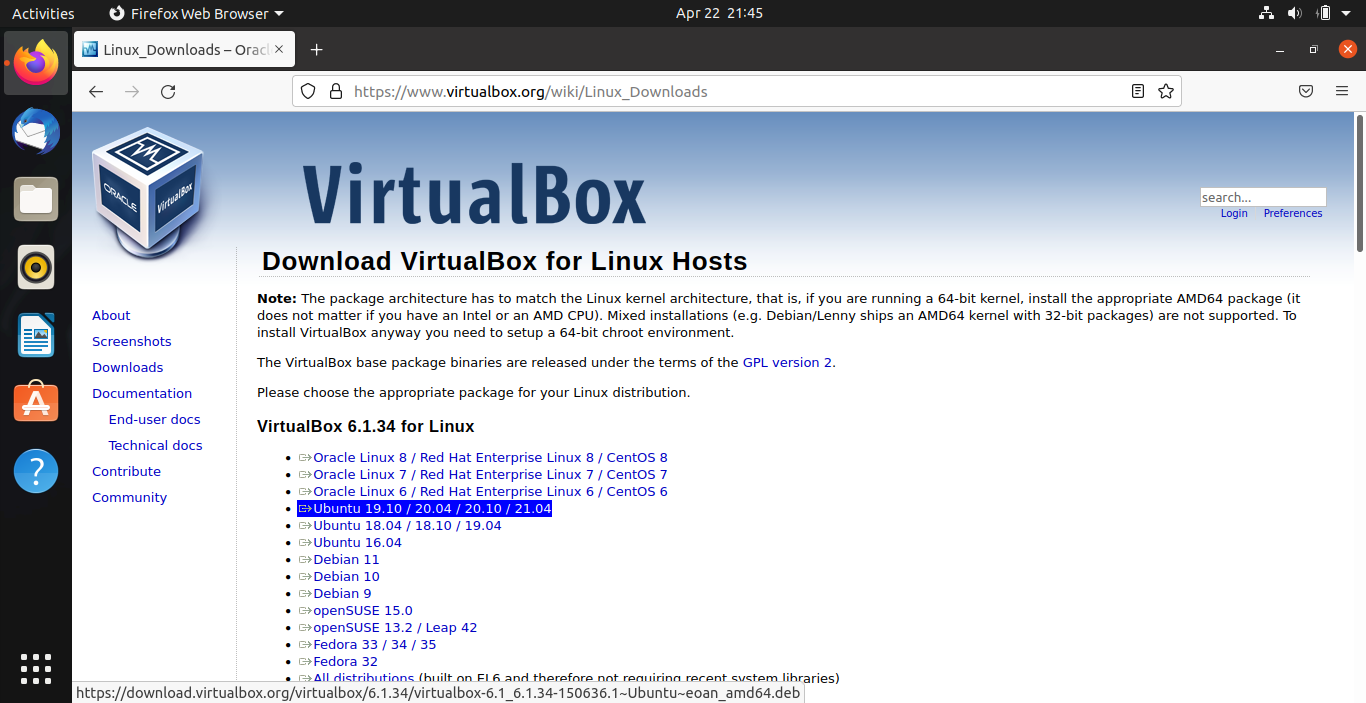
Go to VirtualBox Linux downloads page and click Ubuntu 19.10 / 20.04 / 20.10 / 21.04, but the procedure for other version of Ubuntu is pretty much the same.
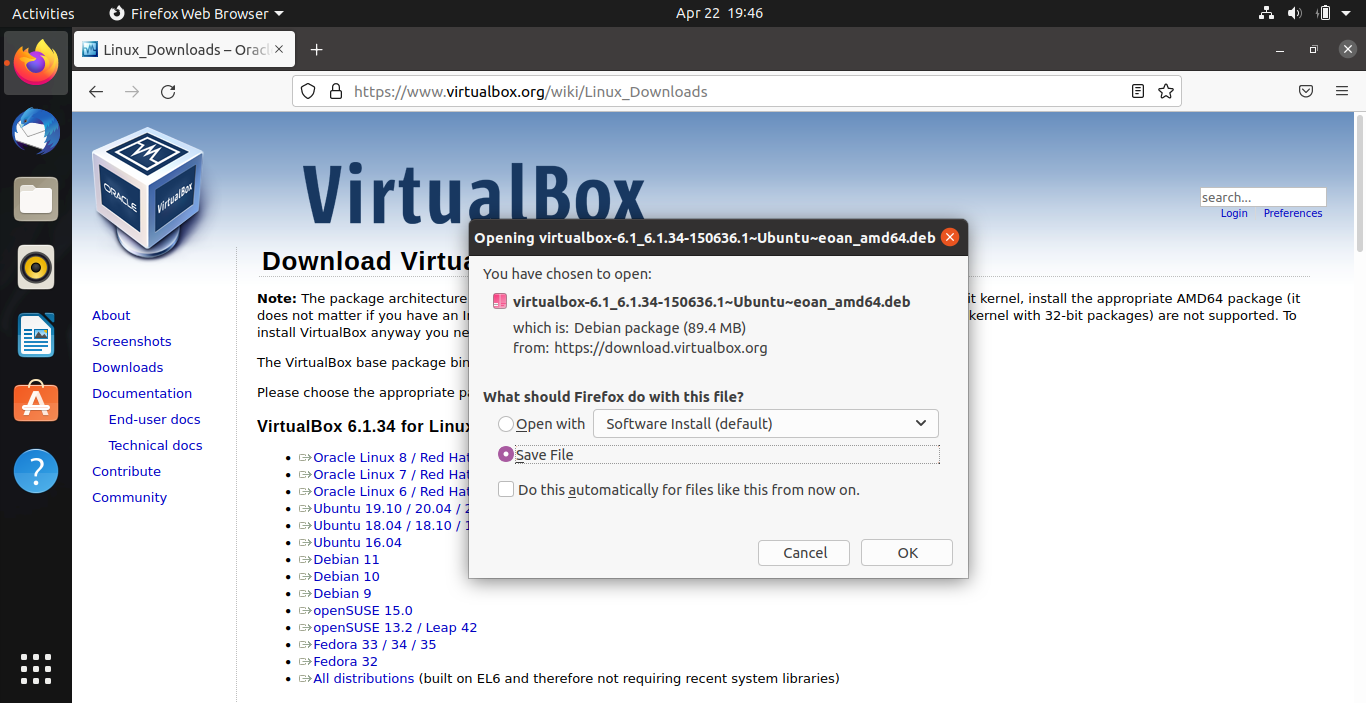
Click save to save the binary.
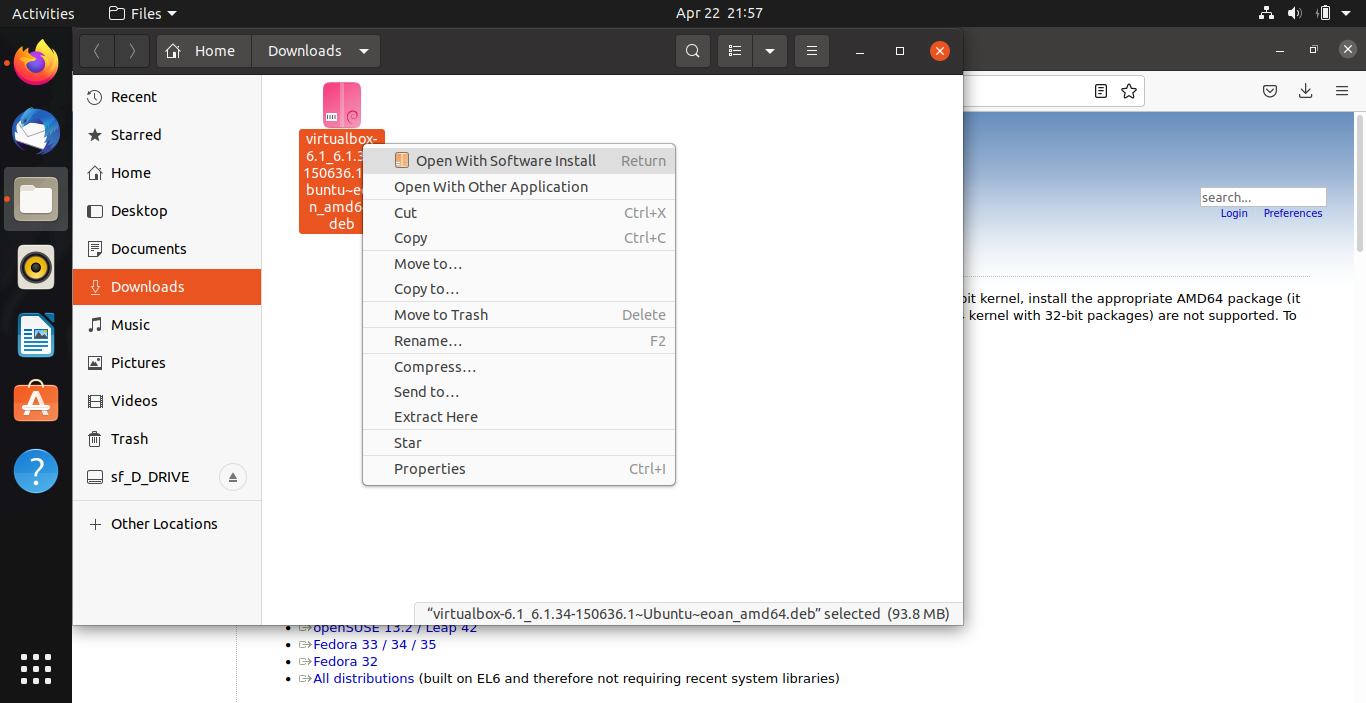
Go to the download location, right-click virtualbox*.deb, then open with software install.
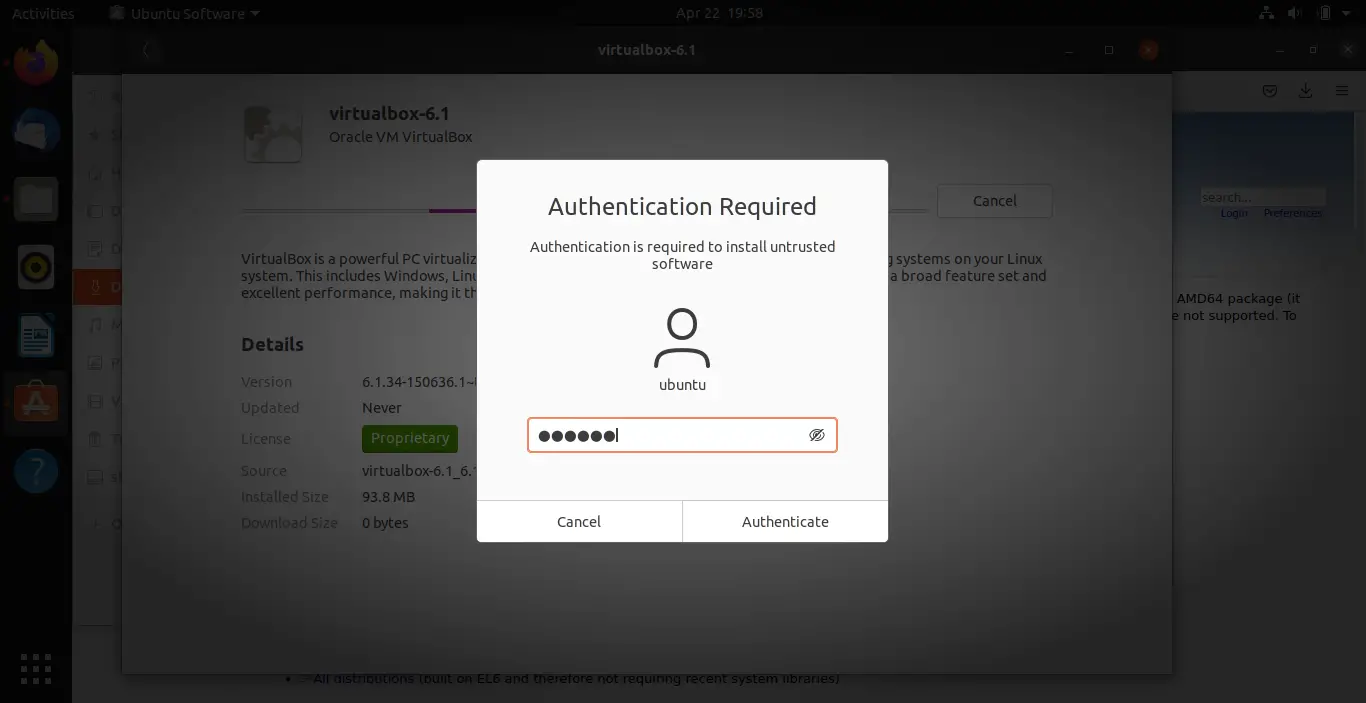
Click install, and pass your password, then press authenticate.
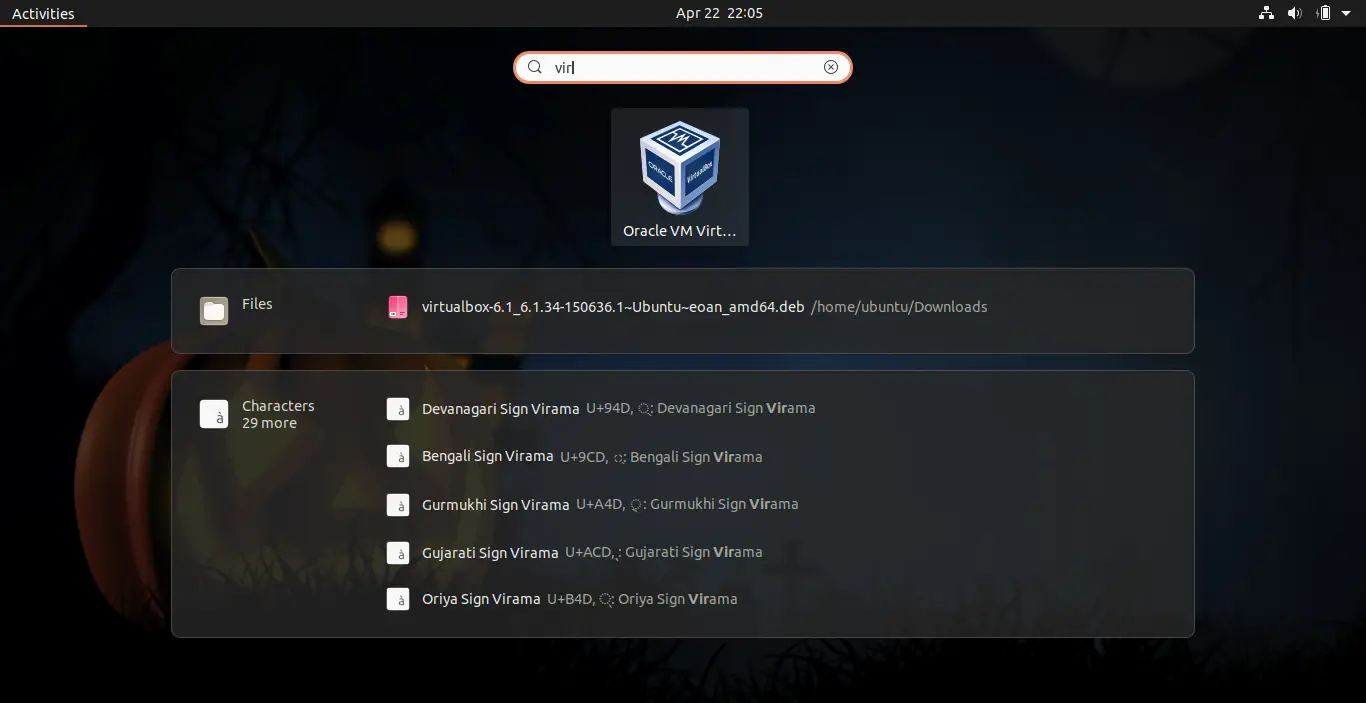
Once done, you can open VirtualBox by searching the app name in your applications.
Installing VirtualBox via the Command-line
VirtualBox is already present in Ubuntu repository, but you will not always find the latest version of VirtualBox.
You need to open a terminal either graphically or by clicking t while holding down Ctrl and Alt keys.
Update apt package list and install VirtualBox:
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y virtualbox
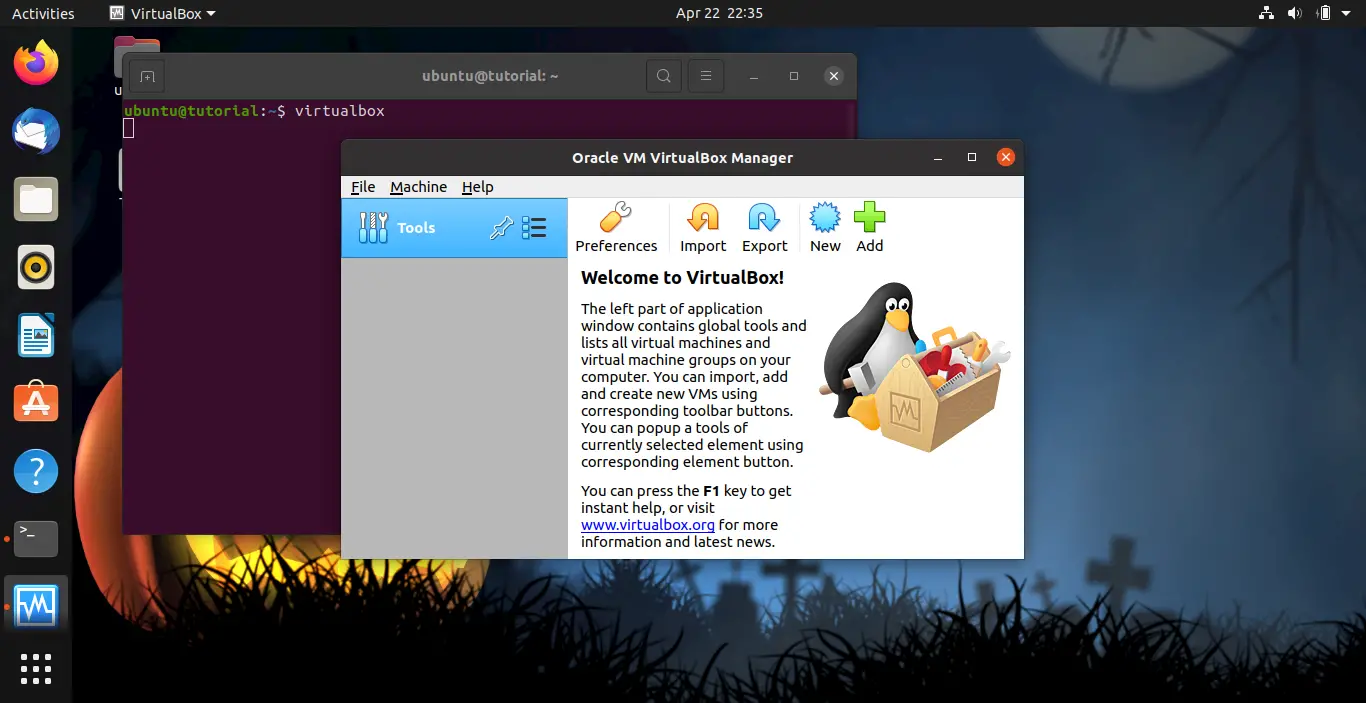
Launch VirtualBox either graphically or by executing the next command.
Install VirtualBox from Oracle Repositories
Open up a terminal either graphically or by pressing t while holding both Alt and Shift keys.
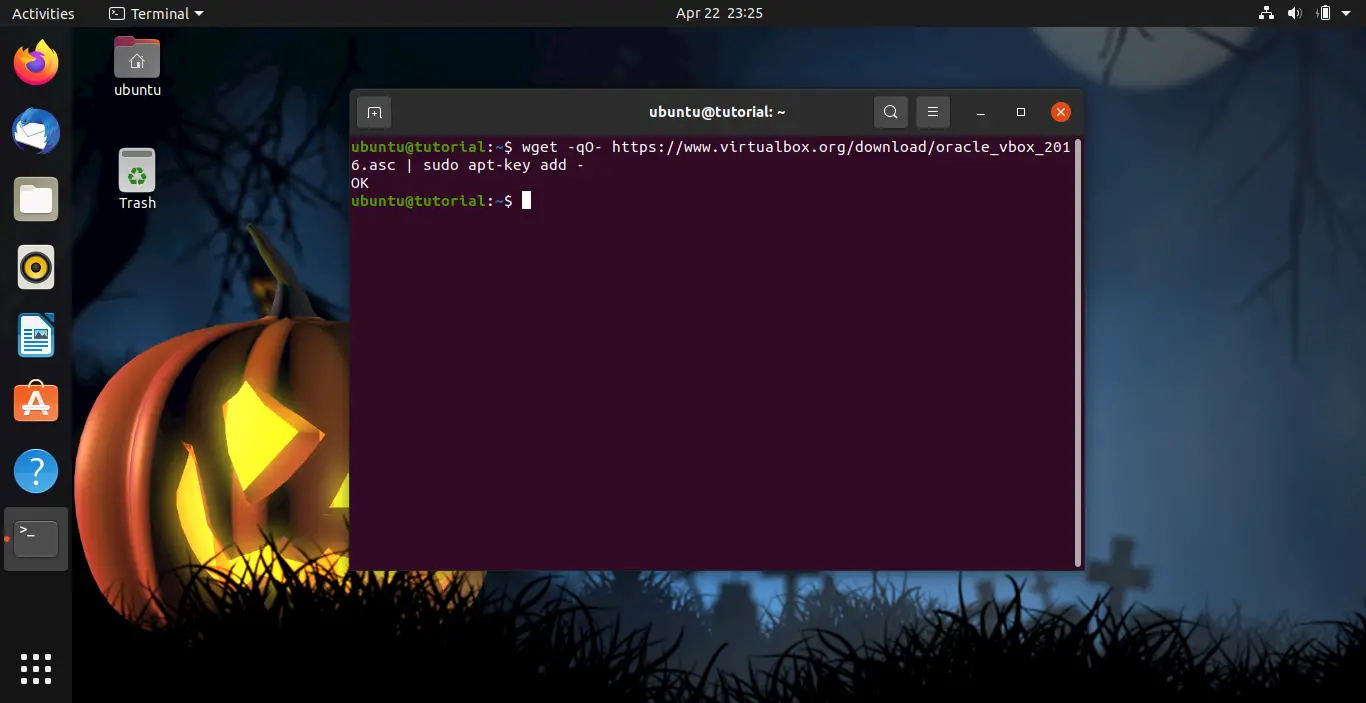
Add the Oracle VirtualBox pgp key to apt using the following command.
wget -qO- https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc | sudo apt-key add -
Add VirtualBox to apt package sources list by adding an entry to /etc/apt/sources.list file (this article will use vim; the entry will be added to the end of the file).
Must be opened the file as root, i.e., with sudo:
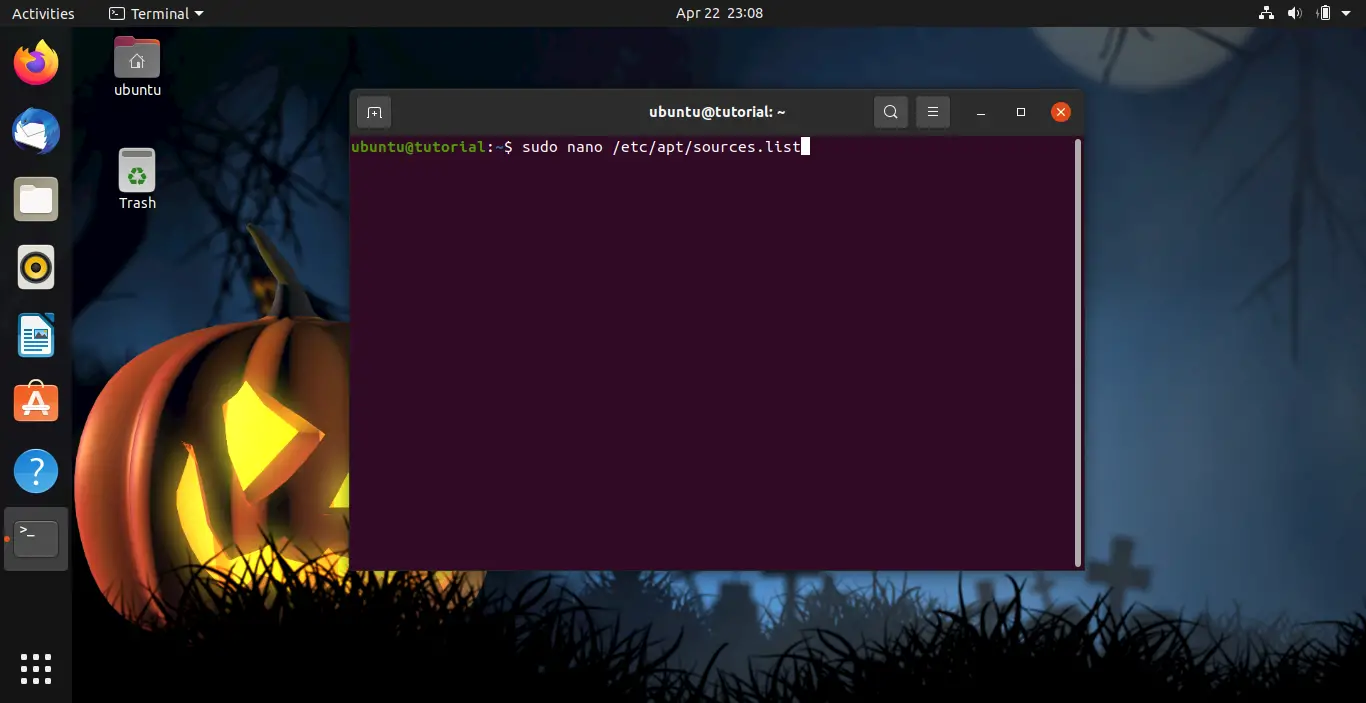
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
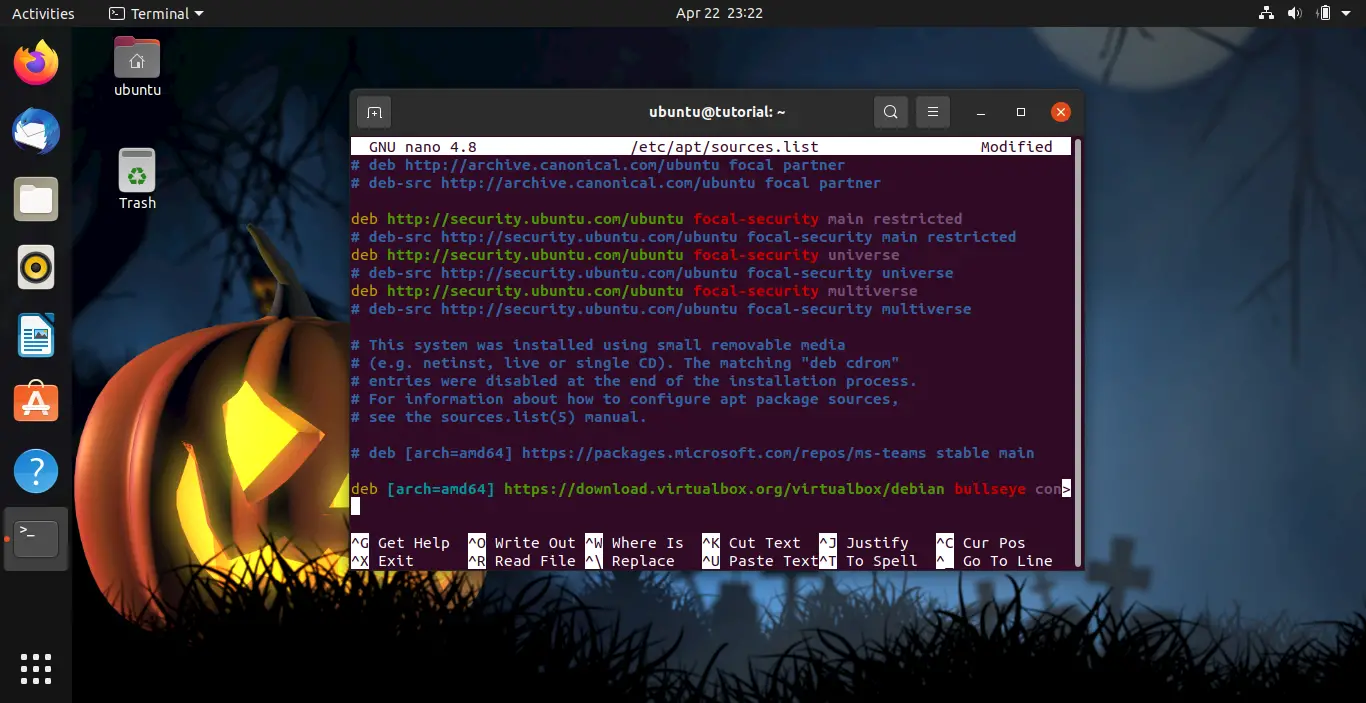
Add the next line to the file, save and exit. Since there is no ubuntu page, we will add Debian’s:
deb [arch=amd64] http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian bullseye contrib
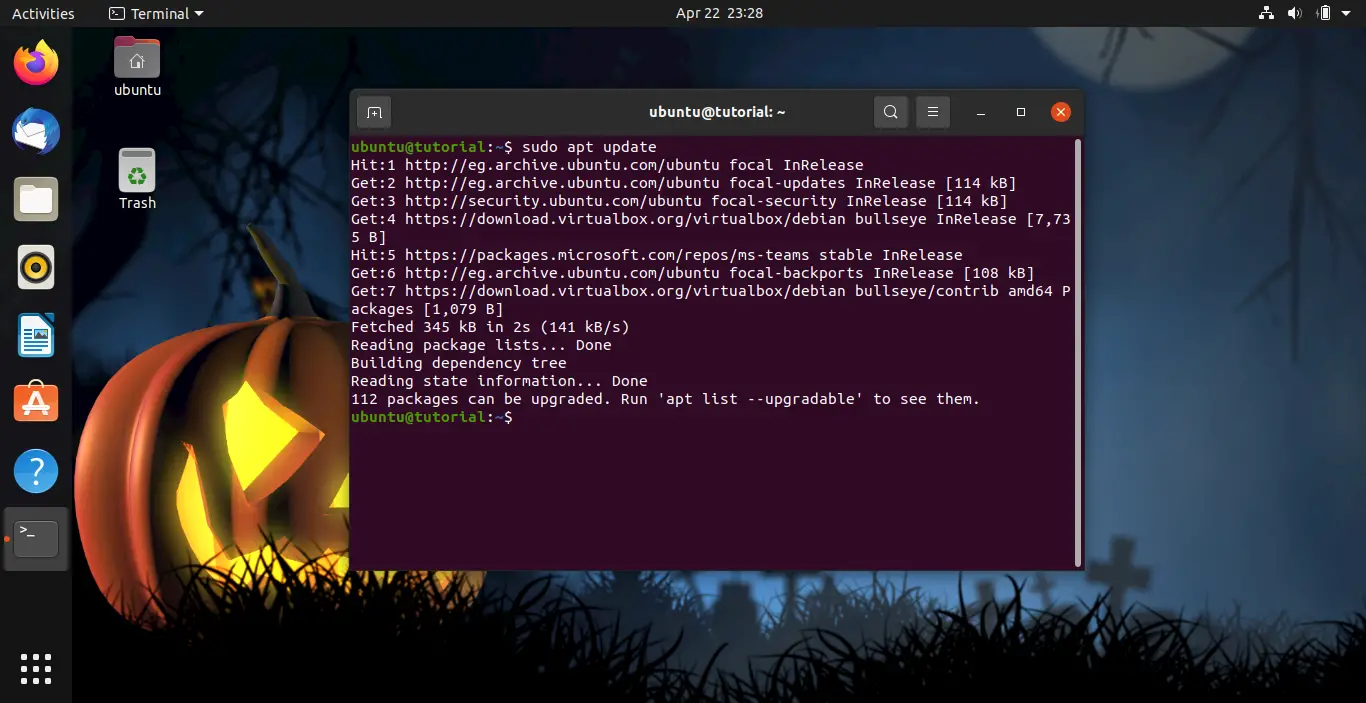
Now update apt package list by running the next command:
sudo apt update
Now install VirtualBox by executing the next command.
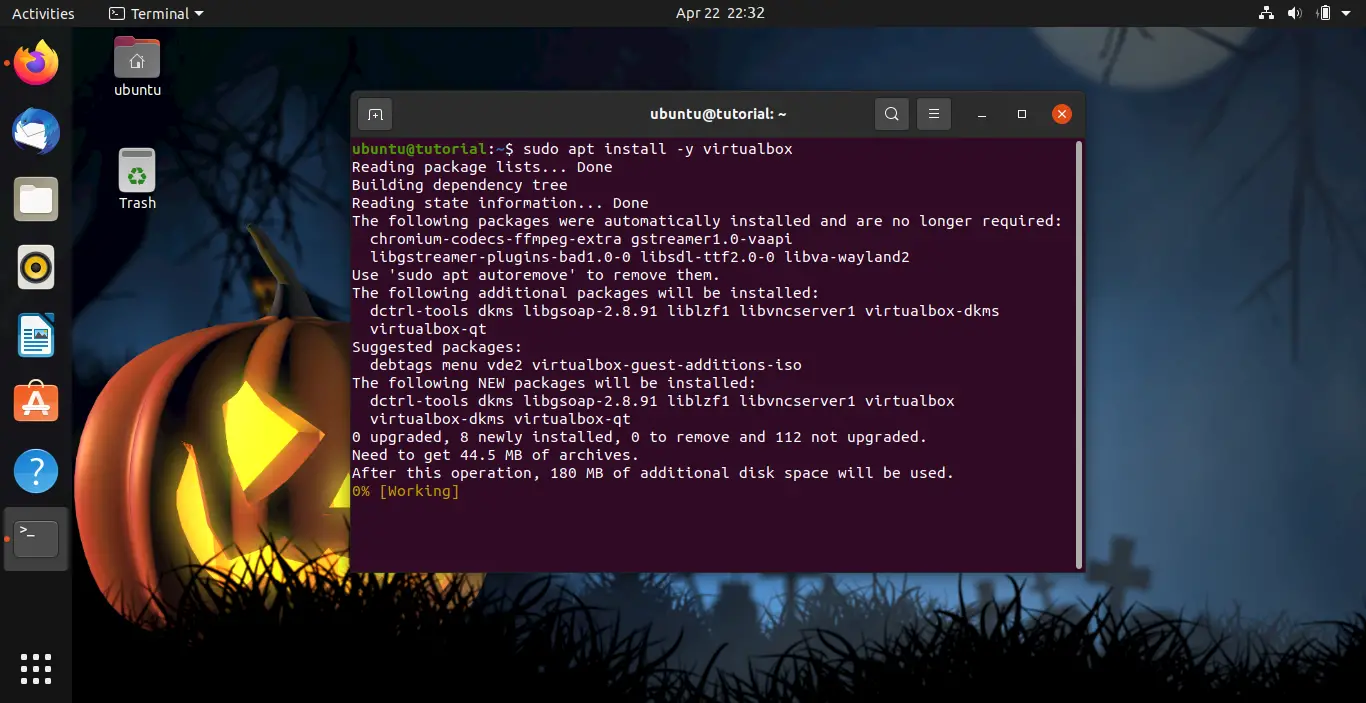
sudo apt install -y virtualbox
Now you can run VirtualBox either graphically by searching your app menu, or by running the next command:
virtualbox
Conclusion
In this article we installed VirtualBox on Ubuntu using the GUI (graphical user interface) method, by installing it from the apt repository, and by installing it from the Oracle repositories. If you have any feedback or questions feel free to leave us a comment.






