You can check the time zone using the timedatectl and date commands or trace the path to the file containing time zone information. You can then change the time zone using the terminal, time zone selection menu or a graphical user interface.
This tutorial helps you change the time zone in Linux using straightforward steps. Read on to learn more.
Table of Contents
Understand Time zones and Standards
A region on earth bound by longitudes is called a time zone. Longitudes are 15 degrees away from one another and run from the North pole to the South Pole, dividing the world into 24 time zones. There exists a time difference of 1 hour between the time zones.
The time zone standards date back to a conference in the International Meridian, which concluded that time starts at Greenwich, London. The system of 24 time zones was named Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). From the 1880s to the 1930s, most countries had synchronized their times with the GMT.
The dawn of the internet in the 1980s saw most operating systems adopt the UTC to ease collaboration among computer programmers and internet users. The time information is stored in the Time Zone (TZ) database, helping to improve consistency when handling the OS or computer programs.
Most countries often change their time zones as influenced by daylight service, economic or political factors. As a result, it is necessary to apply the time zone principles in synchronizing your clock. Let’s see how to do that.
How to check the Time Zone in Linux
The date or timedatectl commands let you view the system’s time.
Let’s head over to the terminal and type timedatectl.
date
OR
timedatectl
The system returns information like your local time, universal time, time zone, NTP service status and whether the system clock is synchronized.
For example, I get the following data.
Local time: Tue 2022-05-24 16:41:22 CEST
Universal time: Tue 2022-05-24 14:41:22 UTC
RTC time: Tue 2022-05-24 14:41:22
Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CEST, +0200)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: no
- Local time is the current time according to your time zone.
- Universal time is the global standard time, measured from the Greenwich meridian. It is also called the Zulu time or universal coordinated time (UTC).
- The RTC time tells the time according to the settings of your operating system.
- My time zone is East African Time, and it is 3 hours ahead of the UTC. The system time zone data gets configured by symlinking the
/etc/localtimefile’s content to the/usr/share/zoneinfodirectory. So, another way to check your local time zone is tolsthe file.
ls -l /etc/localtime
- A system clock synchronized enquiry with a value of yes means the time is synchronized successfully.
- The NTP (Networking time protocol) service synchronizes time between computer systems and the internet’s time servers. My NTP service is active. Yours should, too. However, install it using the ntpdate package if you can’t see yours.
sudo apt install ntpdate
sudo yum install ntpdate
- Lastly, you may also see RTC in local TZ equating to no, meaning the RTC is not available in the local time zone.
Now that you understand the origin of time zones, how to check the current time zone, and time standards, let’s see how o change the time zone.
Top 3 ways to Set/Change time zone in Linux
The three ways to set the time zone in Linux are using the terminal, selection menu or a GUI in Linux desktops like Ubuntu.
1. Set the time zone using the terminal
timedatectl
Local time: Tue 2022-05-24 16:41:22 CEST
Universal time: Tue 2022-05-24 14:41:22 UTC
RTC time: Tue 2022-05-24 14:41:22
Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CEST, +0200)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: active
RTC in local TZ: no
Enter the date command to check your latest time zone on the terminal.
date
Depending on your distribution or previous settings, you should see the date, current time, day, time zone and year. In my case, the system tells me it is the 24th of May; the time is 4:41 pm, Tuesday on Central European Summer Time, and the year is 2022.
Tue May 24 04:41:30 PM CEST 2022
Let’s now view all the time zones before picking the target one.
View all available time zones:
ls -R /usr/share/zoneinfo
Select the target time zone:
tzselect
[powerkit_alert type=”info” dismissible=”false” multiline=”false”]
Note 1. The /usr/share/zoneinfo file may vary according to the distribution.
Note 2. If you can’t see your country in the presented ones, choose the nearby country from the same time zone.
[/powerkit_alert]
On running the tzselect command, the system presents you with the continents to choose your time zone from. Pick the corresponding number, then press enter on your keyboard. For instance, I have chosen 2 for Americas.
A list of countries pops up. Likewise, choose the target country using its corresponding number. For example, I have picked 5 for Bahamas.
Confirm that you want to set the time zone by picking either 1 for Yes or 2 for No. I go for Yes by pressing digit 1 on my keyboard.
Lastly, confirm that the time zone was reset by rerunning the date command. If no, try solution 2 below.
date
Bonus trick
Here is another route to check and change the time zone information on the terminal.
timedatectl list-timezones
sudo timedatectl set-timezone <target time zone>
For Example:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Africa/Nairobi
2. Change the time zone using a selection menu
It turns out the first procedure above changed the time zone temporarily. As guided in the terminal, you can make the change permanent by appending the TZ='<Chosen time zone>' to your .profile file in your home directory.

Alternatively, use the straightforward time zone menu in most Linux distributions.
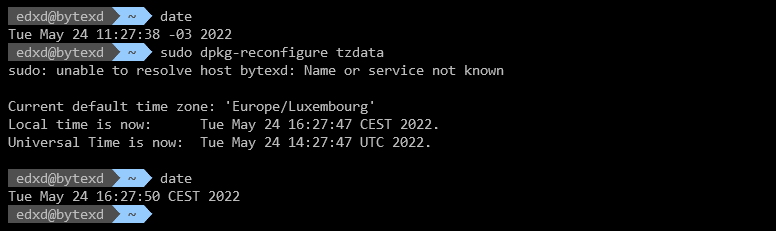
Run the dpkg-reconfigure command with the tzdata option.
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
system-config-date
redhat-config-date
Scroll up or down the presented menu till you meet your geographical area, then press the enter key to select it.
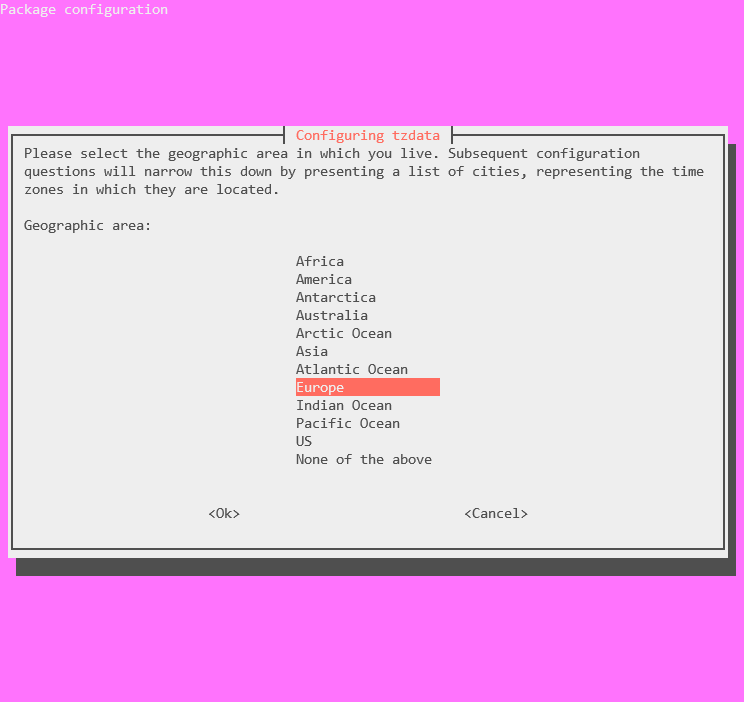
Next, choose the time zone.
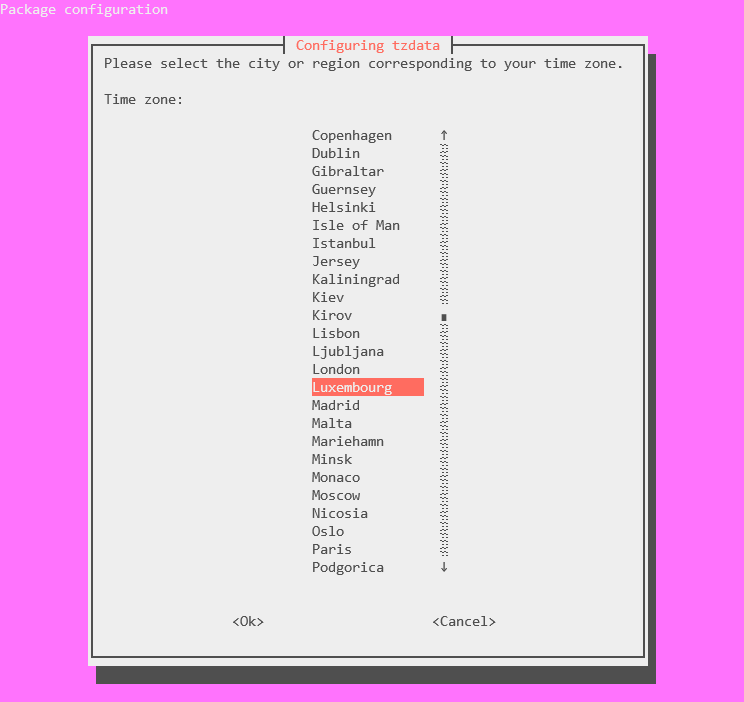
You can then confirm the change using the date command.
And voila, my time zone got changed from -03 to CEST!
3. Change the time zone using a Graphical User Interface
The last way to change the time zone is to use a graphical user interface on some Linux distributions like the Ubuntu desktop.
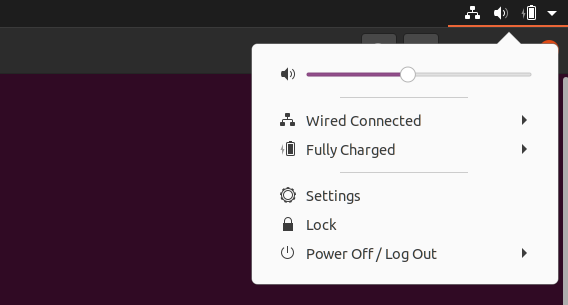
Follow this file path to change the time zone on the Ubuntu desktop: System menu -> Settings -> Date & Time.
Start by clicking the system menu on the top right corner.
Next, click on Settings, then scroll down the left sidebar till you reach Date & Time.
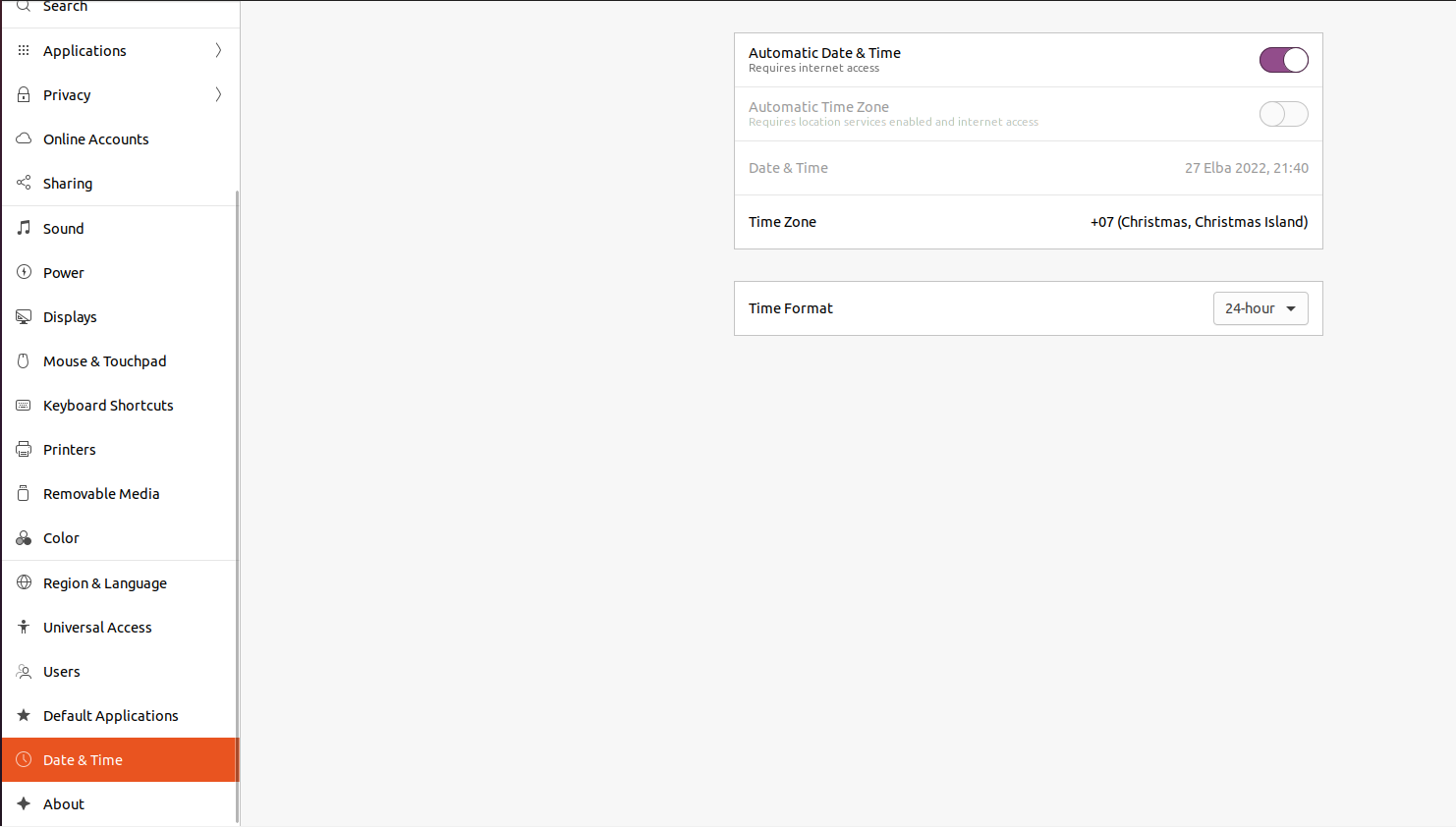
Disable Automatic Date & Time by clicking on the adjacent button till it turns grey.
Click on Time Zone.
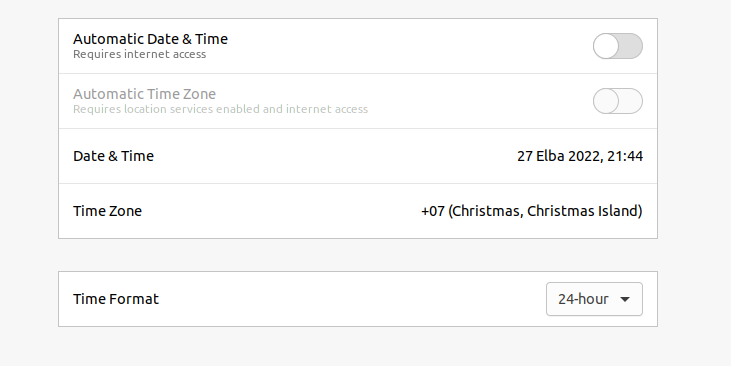
On top of the presented map, search your target time zone or its approximate location.
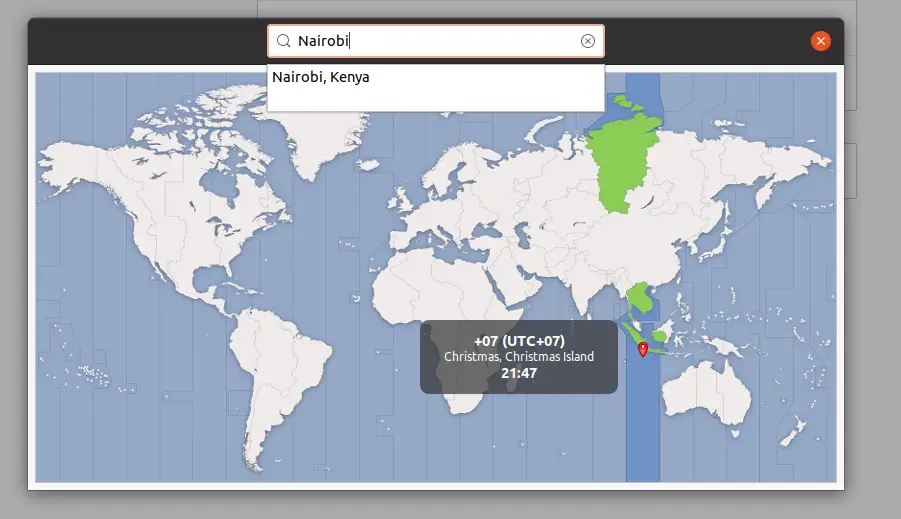
Select it to change the chosen time zone, then close the modal. Now recheck the settings on the terminal using the date command.
date
Tue May 24 14:21:48 EAT 2022
Conclusion
You can check or set/change the time zone in Linux using the terminal, selection menu or the GUI. Choose what suits your Linux distribution and configure its time zone, as guided in this tutorial.