Linux is always regarded as the most secure operating system because the code is open source.
Therefore, researchers and developers can find bugs and send patches, making it much safer over time. However, that doesn’t mean that you sit back, relax, and enjoy the services after installing a Linux distribution like RHEL. No! You need to ensure the system is up-to-date with the latest security updates and patches.
This post will give you a detailed guide on checking and installing the latest security updates for RHEL 6/7/8 systems. We will also show you how to automatically set up your system to install any security updates and patches.
Table of Contents
- What is a Security Patch?
- Identifying security vulnerabilities list
- How to check available security updates on Red Hat (RHEL)
- 1. List Available Security Erratas
- 2. Count the Total Number of Available Erratas
- 3. Security Update List
- 4. Vulnerabilities list with CVE
- 5. Install all Available Security Updates
- Conclusion
What is a Security Patch?
If you are new to all this system-security stuff, you might wonder: What is a security patch? A security patch is a software update that fixes errors and vulnerabilities found in a product to keep everything simple. They are always released by the product company and delivered by updating a part of the software or whole system.
A good example is the recent Apache Log4J vulnerability. This security flaw enabled hackers to bypass any sort of restrictions and gain access to a computer system without the need for a password. Once inside the computer system, they can try installing malicious software, spy on you, or steal critical data. Luckily, Apache developers quickly responded, and they released a security patch to fix the issue.
Identifying security vulnerabilities list
Now you might be wondering – are there frequent reports of security vulnerabilities present on Linux systems? Well, you will be surprised at the number of CVEs reported every month. If you have a Red Hat or OpenSUSE subscription, you will always receive an email detailing all these security issues and updates.
Alternatively, several websites online give you a detailed list of all the reported security vulnerabilities on Linux. Below are some of them:
For example, as of writing this post, the total number of vulnerabilities for March (2022) reported on National Vulnerability Database is 836. See the image below.
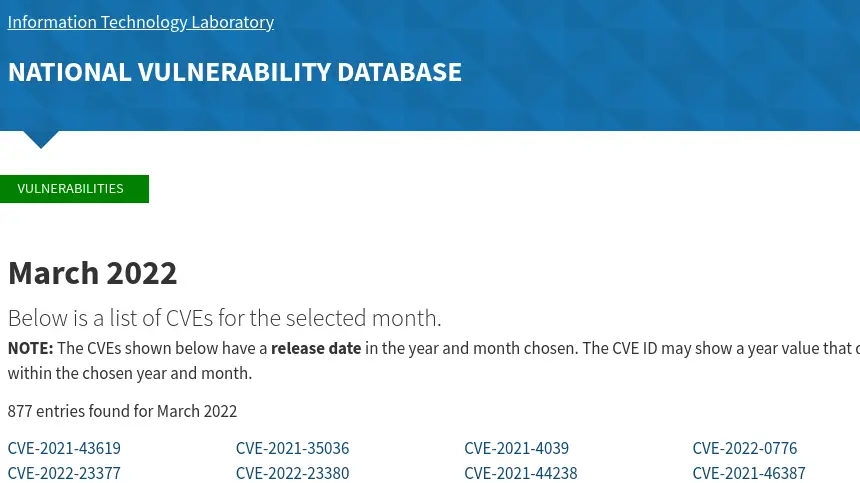
You realize from the report above how hard it is to individually go through all these CVEs and patch your system manually. That’s why you are always recommended to scan your systems regularly to identify all the security vulnerabilities and install the updates accordingly.
Additionally, there are third-party tools that you can use to scan your system for vulnerabilities and install the security updates automatically. Some of them include
- Nessus
- Qualys Guard
- IBM App Scanner
- Nmap
- Accunetix.
How to check available security updates on Red Hat (RHEL)
Up to this point, I believe you now understand the importance of scanning for vulnerabilities on your system, websites where you can check for all reported CVEs, and some of the tools you can use to scan and install security updates on your systems. Now, let’s look at how you can check for available security updates on your RHEL system.
We will use the yum package manager present on RHEL systems to simplify everything. Install the Yum Security Plugin by executing the commands below depending on your RHEL distribution.
RHEL 6 and CentOS 6
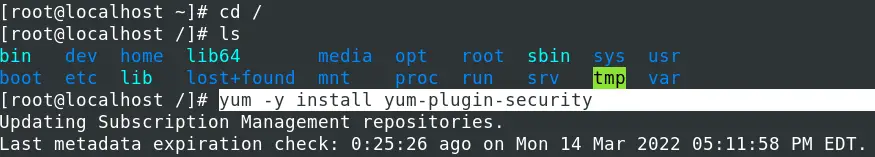
Execute the command below.
yum -y install yum-plugin-security
RHEL 7/8 and CentOS 7/ 8
This plugin comes as part of Yum on RHEL 7/ 8. Therefore, you don’t need to install it manually. Now, execute the commands below depending on what you want to achieve.
1. List Available Security Erratas
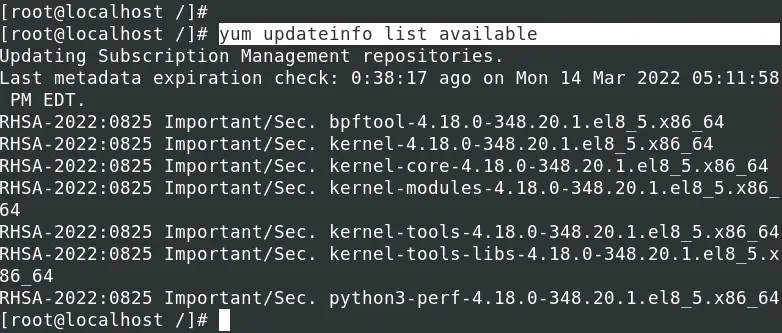
Execute the command below to list all available security errata without installing. That includes security, software/ product enhancement, and bug fixes.
yum updateinfo list available
2. Count the Total Number of Available Erratas
If you want to know the total number of security errata you need to download, you can pipe the output of the command above to the wc command as shown in the image below.
yum updateinfo list available | wc -l

We had recently done a security update on our system hence the low number of security errata (in our case it’s 9). On other systems, this number may go as high as up to 10,000.
3. Security Update List
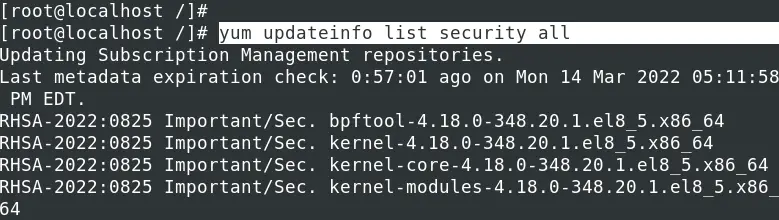
Execute the command below to get a list of all RPMs from the security update list without installing them.
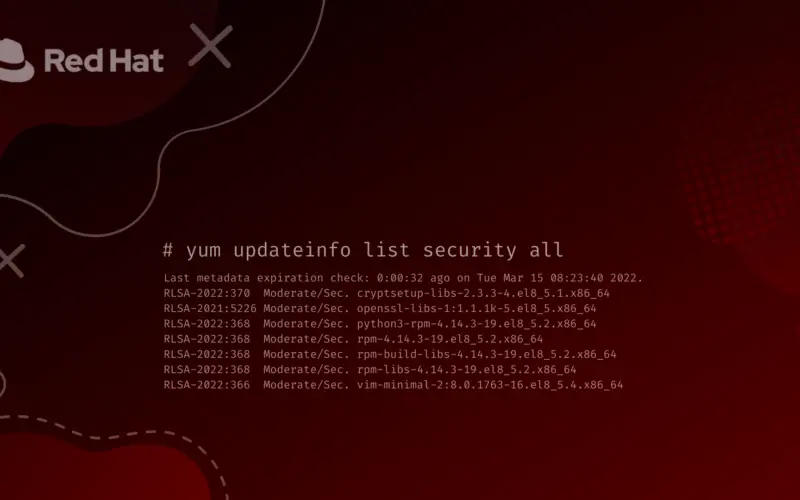
yum updateinfo list security all
To view all the RPMs from the currently installed security updates, execute the command below.
yum updateinfo list security installed
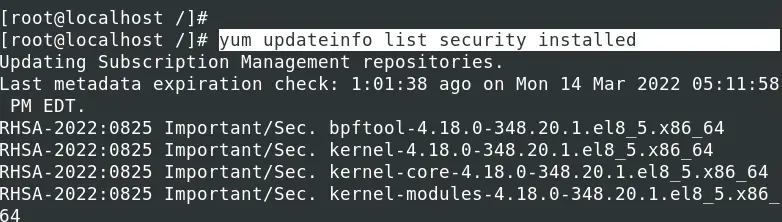
To get more information about any security update before applying the patch, use the syntax below.
yum updateinfo [Patch-ID]
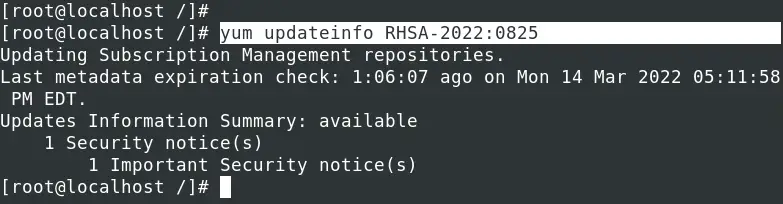
E.g.
yum updateinfo RHSA-2022:0825
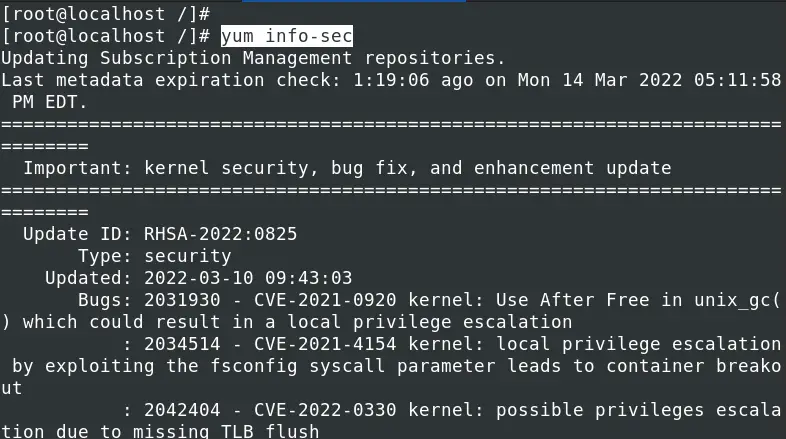
To view all the security update list together with detailed information of the issues they are applying execute the command below.
yum info-sec
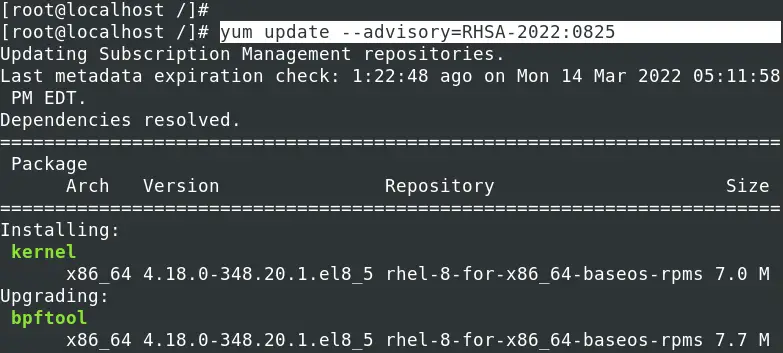
To install a security patch for a particular advisory listed by the command yum updateinfo list available, use the syntax below.
yum update --advisory=[Patch-ID]
E.g.
yum update --advisory=RHSA-2022:0825
4. Vulnerabilities list with CVE
To get a full list of all reported CVEs that could impact your system, execute the command below.
yum updateinfo list cves
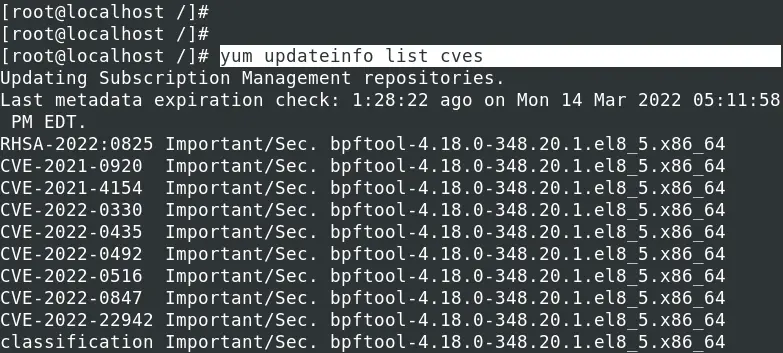
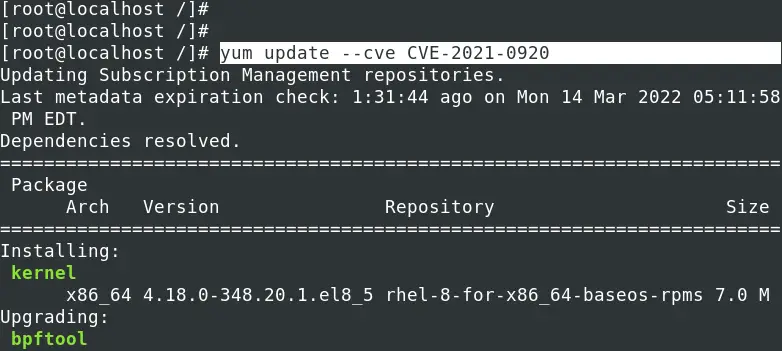
To install a security patch for a particular CVE, use the syntax below.
yum update --cve [CVE-ID]
E.g.
yum update --cve CVE-2021-0920
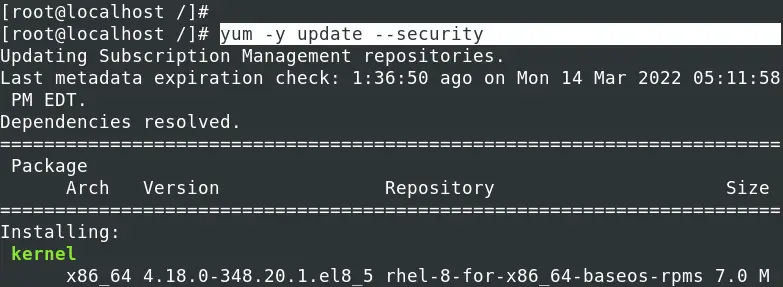
5. Install all Available Security Updates
To install all the available security updates provided by Red Hat for your system, execute the command below.
yum -y update --security
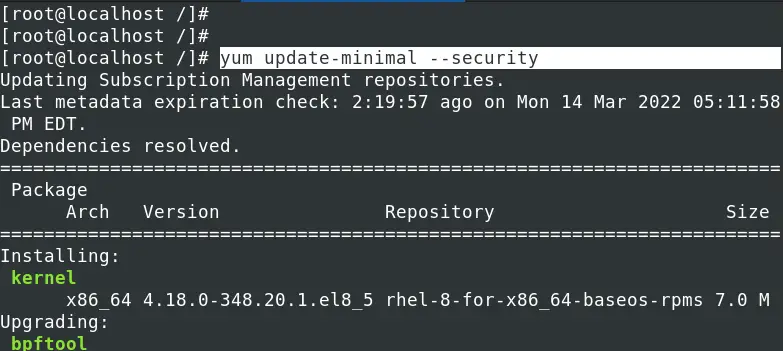
If you wish to install only packages with security errata use, execute the command below.
yum update-minimal --security
Conclusion
I hope these steps gave you an overview on Linux security errata, security update list, CVEs, and applying Linux security updates on RHEL Linux. Did you encounter any errors or need any clarification regarding the steps described above? If Yes, please don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.