The whatis command in Linux is used to display the brief manual page description of Linux commands. The manual page contains a detailed description of each specified command or option. So, we can say that it helps you to provide a quick short description of a Linux command. It searches for the arguments from its index databases that are provided with the whatis command to view the short manual page description.
In this article we’ll explore using the whatis command. We can also use whatis along with different options.
whatis command syntax
The syntax of the Linux whatis command is
whatis [OPTION] [KEYWORD]
Use of whatis command
Most users don’t know about the purpose of the whatis command. When we want to display the short one-line summary of a Linux command, the Linux whatis command in this case helps us. Linux whatis command displays an error if no option or an argument is passed. Therefore, it is necessary to use a Linux command or an option as an argument with the whatis command. Let’s take a simple example to explain the use of the whatis command.
whatis mkdir
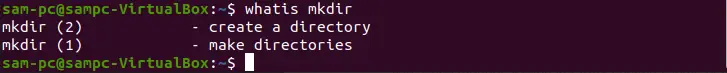
This displays the manual page description of the mkdir command in a single line.
Similarly, to print the short description of the head command, the whatis command can be used in the following way:
whatis head

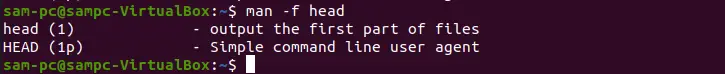
If we will use the -f option with the man command then, it will also produce the same result.
man -f head
Display information or description of multiple commands
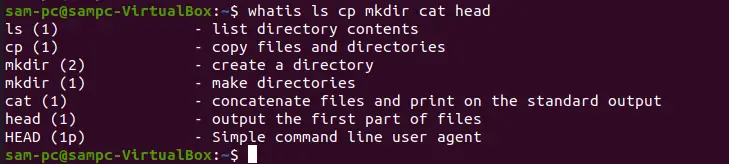
To display a brief manual page description of multiple Linux commands, we can use the whatis command in the following way:
whatis ls cp mkdir cat head
whatis command Options
In this section, we will explore the different options of the Linux whatis command by using various examples.
-h or -? – Display help
To display help about the whatis command, we can use the -? or -h.
whatis -h
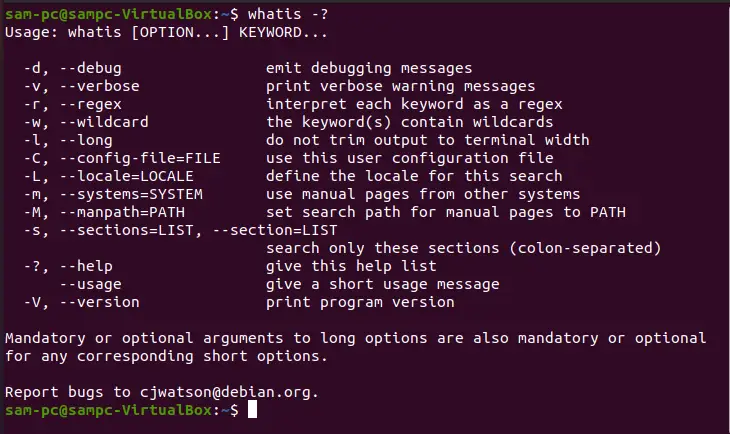
This command shows the various options on the terminal that we can use with the whatis command for more details.
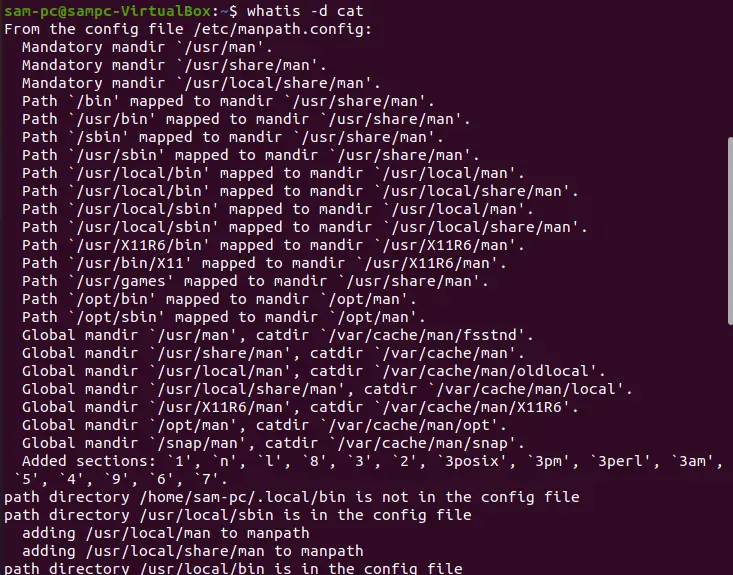
-d or --debug – Debug information
This command displays the debugging details of a Linux command on the terminal.
whatis -d cat
-w or --wildcard – keywords contain wildcard
This option interprets each keyword name as a pattern that contains the wildcards. For an exact match, the extended entire page name should be matched.
whatis -w cat

-v or --verbose – verbose warning messages
It prints the verbose details or warning message about the Linux command.
whatis -v cat

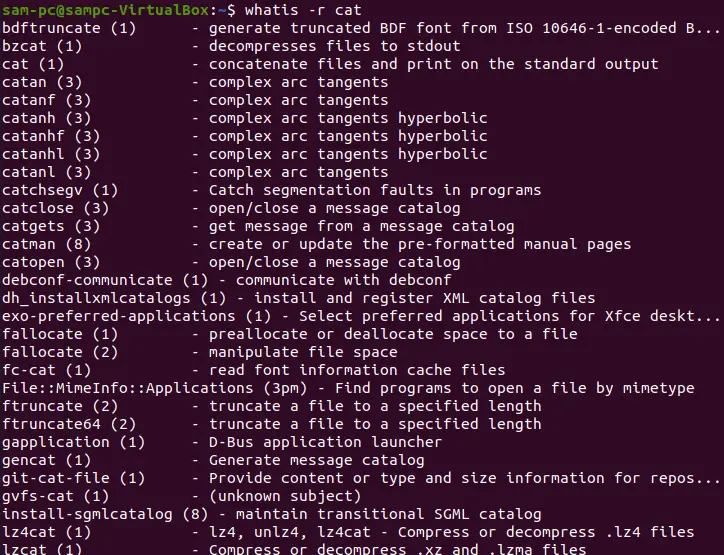
-r or --regex – Interprets each keyword as regex
This option takes each keyword name as a regular expression and if any keyword name matches any part of a manual page, it returns this match.
whatis -r cat
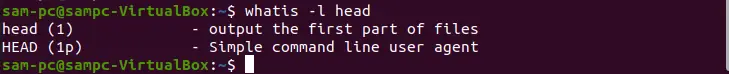
-l or --long – do not trim the output with terminal width
This option does not trim or cut the output with the terminal width.
whatis -l cat

whatis -l head
-s or --section=List – search only colon-separated sections
The -s option is used to search the specified manual sections. The section list is divided by a comma or colon-separated. If an entry in a list contains any perspective section. Then it shows the details of a given keyword. Otherwise, it displays a messagenothing appropriate:
whatis -s cat

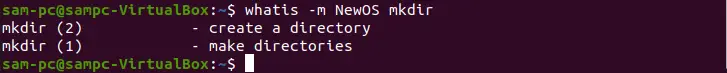
-m or --system=SYSTEM – Use manual pages from Other OS
Using the -m option, our system can access the other system’s manual page names. For example, we want to search names of NewOS’s manual page, in this case, we can use this option as -m NewOS.
whatis -m NewOS mkdir
-M or --manpath=PATH – set search path for manual pages
This option sets the search path for manual pages for Path which means it allows you to browse using a set of colon-delimited manual page hierarchies. Linux whatis command by default uses the $MANPATH environment variable.
whatis cat -M --manpath=/lib/cat

-L or --locale=LOCALE – temporarily overrides the determined value
The -L option overrides the determined value or keyword temporarily. This option is used to directly supply the locale string to the whatis command. This action will not have any effect on the search for manual pages.
whatis cat -L locale

-C or --config-file=FILE – use this user configuration file
The -C option is used for using the user configuration file instead of using the default ~/.manpath.
whatis -C file
-V or --version – display program version
This option is used to display the installed program information or Linux command version on the terminal.
whatis -V

--usage – Print usage details
To view the basic use of the whatis command, use the following command:
whatis --sage
This command will display the short usage message on the terminal.
Conclusion
We explored how the Linux whatis command works in a Linux system. We have seen different uses and options of the Linux whatis command in this article. Moreover, we discussed how the whatis command is used with other Linux commands. I hope this tutorial will be informative and useful for you. Send us your feedback if you like this article. Thanks!






![How to Install and Use Telnet on Linux 72 telnet [options] host [port] on light blue background](https://bytexd.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/How-to-Install-and-Use-Telnet-on-Linux-380x220.png)