In the past, you needed Thunderbolt if you wanted to connect an external GPU to your laptop, but things have changed now that USB4 has been introduced. Since USB4, Thunderbolt 3, and Thunderbolt 4 all have the same connectors and similar specifications, differentiating between the three can be tricky. This article covers the differences between these connection interfaces and covers whether you can use USB4 with external GPUs.
USB4 vs Thunderbolt 3 vs Thunderbolt 4
USB4 uses the USB-C connector and has data transfer speeds of up to 40Gbps. It has similar functionality as Thunderbolt 3 and supports DisplayPort and DisplayPort Tunneling to use with an external graphics card. USB4 does not require an Intel-certified controller and is royalty-free. Note that while USB4 can support external GPUs, this mainly depends on the USB4 implementation. This is also true for Thunderbolt 3 compatibility and other features. Regarding speed, the minimum requirement for the USB4 standard is 20 Gbps. So, you might not get the full 40 Gbps transfer speed despite having a USB4 interface.
Thunderbolt 3 also uses the USB-C connector and supports data transfer speeds of up to 40Gbps. Like USB4, Thunderbolt 3 supports protocols such as DisplayPort and PCIe for external GPUs. And it supports either a single 4K display at 120Hz, a 5K display at 60Hz, or two 4K displays at 60Hz. It is worth mentioning that some Thunderbolt 3 are limited to 20 Gbps so you should check the rated speed before buying. Thunderbolt 3 is proprietary to Intel and requires an Intel-certified controller.
On paper, Thunderbolt 4 has the same maximum speed as USB4 or Thunderbolt 3. It does require a controller and certification from Intel. The changes are oriented toward quality control since Intel further requires the Thunderbolt 4 standard to support the full 40 Gbps speed. So, you no longer need to worry about accidentally buying a cable that is limited to 20 Gbps. Furthermore, Intel requires Thunderbolt 4 to support two 4K displays or a single 8K display.
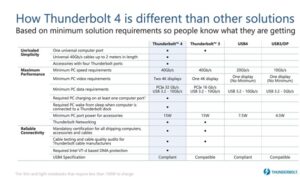
Image Credit: Intel
These ports also come with additional features such as support for accessories, PC charging, wake from sleep, and Thunderbolt networking.
While all three might have similar specifications on paper, Thunderbolt 4 is more reliable and has higher minimum specifications. While manufacturers can choose to cut costs by not implementing some features with USB4, Thunderbolt 4 doesn’t have any such provision.
If you are having trouble with Thunderbolt on Linux, you can check out our guide on how to use Thunderbolt 3 and 4 on Ubuntu.
Do USB4 eGPUs Exist?
Using an eGPU with a USB4 port depends on whether the implementation conforms to Thunderbolt 3 specifications. For example, AMD Ryzen 6000 series chips do not support Thunderbolt 3 even though they have USB4. Manufacturers need to add additional hardware to enable Thunderbolt 3.
If you are interested in using an external GPU with your laptop and cannot figure out the technicalities, then buy an Intel-based Thunderbolt laptop. But if you understand these technologies well and want an AMD-based laptop, you must ensure that the USB4 port supports the full 40Gbps transfer speeds. Moreover, if your laptop’s USB4 implementation allows it, you can use Thunderbolt 4 eGPU setups. Check out our recommended Thunderbolt eGPU enclosures to pair with your USB4-enabled AMD laptop.
Table of Contents
Comparison of the Best USB4 Compatible eGPUs
| Image | Product | Details | Check Price |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Razer Core X Aluminum | Data Transfer Speed: 40Gbps Interface: Thunderbolt 3 (Compatible with USB4) Number of Ports: 1 Internal Power: 650W Power Delivery: 100W GPU Included: No USB-A Port: None | Buy on Amazon |
 | Akitio Node Titan | Data Transfer Speed: 40Gbps Interface: Thunderbolt 3 (Compatible with USB4) Number of Ports: 1 Internal Power: 650W Power Delivery: 85W GPU Included: No USB-A Port: None | Buy on Amazon |
 | Sonnet eGPU Breakaway Box 750 | Data Transfer Speed: 40Gbps Interface: Thunderbolt 3 (Compatible with USB4) Number of Ports: 1 Internal Power: 750W Power Delivery: 100W GPU Included: No USB-A Port: None | Buy on Amazon |
1. Razer Core X Aluminum – Our Choice
The Razer Core X Aluminum is our choice for the best eGPU you can use with your AMD laptops. It combines a subtle design with a powerful 650W PSU that’ll power the most demanding PSUs while ensuring the enclosure remains ventilated enough to prevent thermal throttling.
The Core X Aluminum has a maxed-out spacious design that enables you to accommodate a 3-slot wide GPU fully loaded with multiple fans. So you won’t feel restricted while choosing a GPU that suits your needs. The enclosure has a convenient pull-out tray design, making it super convenient to access the PCIe slot when installing (or uninstalling) the GPU. The rear panel has a quick-release handle that makes the process easy while ensuring the device occupies minimal space at your workstation.
On the technical side, the Core X has a Thunderbolt 3 interface that is entirely compatible with USB4 and delivers 40Gbps data transfer speed. So, apart from using it with a Thunderbolt laptop, you can pair it with any AMD laptop using a fully functional USB4 port that supports 40Gbps data transfer speed. The lone Thunderbolt 3 port is located on the enclosure’s rear panel and offers 100W Power Delivery to charge the most power-hungry laptops on the market.
The Core X’s versatile compatibility is also its most remarkable feature. You can use both Nvidia and AMD GPUs to set up your ideal gaming rig, and the enclosure is also compatible with any Mac computer running on macOS 10.13.4 or later.
- A Versatile device compatible with most GPUs and works well with macOS.
- The 100W Power Delivery is perfect for charging power-hungry laptops.
- The quick-release handle and pull-out tray design provides convenient access to the GPU.
- Plenty of internal space to accommodate bulky GPUs.
- The ventilated design ensures the device remains cool at peak GPU performance.
- Expensive
- The device lacks proper gaming aesthetics.
- Razer’s poor customer support.
2. Akitio Node Titan – Cheapest
The Akitio Node Titan is the most pocket-friendly eGPU enclosure for your USB4 laptop. But cheap doesn’t mean the Titan offers less than its rival devices. This enclosure from Akitio offers all the essential features of a good eGPU enclosure without burning a hole in your pocket.
The Titan uses a Thunderbolt 3 interface to offer a 40Gbps data transfer speed and power delivery. It has a generous 650W PSU that’ll power even the most demanding GPUs on the market. And its compatibility with macOS and Windows ensures you get the flexibility of choice while choosing your gaming rig. Most importantly, its 85W Power Delivery ensures your laptop’s battery will never run out of charge as long as you are connected to the device.
The enclosure is bulky and is the same size as commonly used CPU cabinets. This means you’ll require plenty of room on your workstation to accommodate this huge eGPU enclosure. On the bright side, the bulky exterior also ensures that you have plenty of internal room in the enclosure to accommodate a double-width GPU card.
Moreover, the design of the Akitio Node Titan makes excellent use of the additional space to pair it with convenient comfort. The design includes a retractable handle that conceals itself into the enclosure’s top panel, making it convenient to carry the device when needed.
Its side wall mesh design facilitates efficient airflow, keeping your GPU from overheating during prolonged hours of gameplay. You won’t need tools, as Akitio has made it easy to access and install GPUs by including thumb screws that you can access on the rear panel.
- The 85W Power Delivery will charge most laptops.
- Price
- Enough power to handle most high-performance GPUs.
- Plenty of internal space to accommodate bulky GPUs.
- The ventilated design ensures the device remains cool at peak GPU performance.
- The bulky design occupies too much space on the workstation.
- No pull-out tray makes aligning the GPU with the PCIe slot challenging.
3. Sonnet eGPU Breakaway Box 750 – 750W PSU
The Sonnet eGPU Breakaway Box 750 offers a 750W PSU, which is amongst the highest you’ll find on such devices. However, its design may cause you some grief as you’ll find it challenging to accommodate bulkier GPUs in its surprisingly small body.
It’s loaded with all the right tech and offers a fully functional Thunderbolt 3 interface that’s compatible with USB4 (at 40Gbps) ports. You also get 100W Power Delivery that’ll ensure your laptop doesn’t run out of charge. In fact, the Sonnet Breakaway Box 750 is AMD-approved for a few of their air-cooled GPUs.
It is compatible with both Nvidia and AMD GPUs, provided you can accommodate them in the box. Sonnet also includes two 8-pin (6+2 pin) connectors for auxiliary power, so you can use power-hungry GPUs to curate the perfect gaming rig.
The Sonnet 750 is a versatile eGPU enclosure for most parts. It is compatible with all Windows-based computers and Intel-based Macs. Unfortunately, the Sonnet 750 is incompatible with Mac computers running the M1 processor. But those compatibility issues are peculiar to Apple. It is not a flaw of the Sonnet 750.
It delivers fantastic performance while using popular editing tools like DaVinci Resolve, DaVinci Resolve 15, and Adobe Premier Pro.
- The 750W PSU provides plenty of power for demanding GPUs.
- The 100W Power Delivery will charge most laptops.
- Price
- Versatile device compatible with most GPUs and works well with macOS 10.13.6 and later.
- Super quiet at peak performance makes it ideal for work environments.
- The small chassis can’t accommodate bulkier GPUs.
- No pull-out tray makes aligning the GPU with the PCIe slot challenging.
USB4 eGPU – Frequently Asked Questions
Are USB4 Laptops Compatible With Thunderbolt 3 eGPUs?
Whether or not a Thunderbolt 3 eGPU enclosure will work with a USB4 laptop depends on the laptop manufacturer. Since PCIe tunneling and Thunderbolt 3 support are optional for the USB4 specification, there is no guarantee that the Thunderbolt 3 eGPU will work. It all comes down to the specific implementation of the USB4 port. The Apple M1 pro models, for example, are compatible with Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4, but that might not be the case with other laptops.
Do Thunderbolt 4 eGPUs Exist?
External graphics card enclosures support Thunderbolt, such as the eGPU Breakaway Box 750/750ex. While eGPU enclosures can use Thunderbolt 4, as mentioned above, it has the same maximum speeds as Thunderbolt 3. Thunderbolt 4 ensures that you get better minimum transfer speeds of 40 Gbps and are not limited to 20 Gbps.
Jarrod’sTech tested the performance of an eGPU in different games and concluded that the performance improvement depends more on the CPU’s performance rather than the Thunderbolt implementation. Hence, you won’t experience performance loss using Thunderbolt 4 or Thunderbolt 3.
Do Laptop eGPUs Perform As Well As Dedicated Desktop Graphics Cards?
Dedicated graphics cards in laptops are not as powerful as their desktop counterparts since they are limited by power and the thermal design of the laptop.
So, are desktop graphics cards paired with laptops via eGPU enclosures on par with desktop graphics cards?
Jarrod’sTech tested a couple of games with eGPUs, compared them to desktop graphics cards, and found that the graphics cards used in a desktop perform better than cards connected to laptops via external GPU enclosures.

It all comes down to how much you value portability. You can turn a thin and light laptop, without a dedicated graphics card, into a gaming machine using an external graphics card enclosure. On the downside, an eGPU setup can be very expensive, and you might find that getting a mid-range laptop or desktop costs the same.
Do AMD Laptops Come Only With USB4?
Any laptop manufacturer can use Intel’s Thunderbolt standard under a licensing agreement. So, while you can find AMD-based laptops with Thunderbolt ports, they are uncommon. Thus, you can remain loyal to the AMD platform and still consider gaming using an eGPU setup using Thunderbolt.

Conclusion
Thunderbolt 3 support is optional for the USB4 specification, so using an eGPU with USB4 won’t always be possible. Sure, if you have the right USB4 implementation that offers a high PCIe bandwidth, you can have your pick of eGPUs and enjoy gaming on your ultrabook. But there are only a handful of options on the market that offer the said USB4 specifications.
So, it is improbable, and your best bet remains an Intel-based laptop with Thunderbolt 4 for connecting an eGPU. The market is filled with plenty of options to suit any budget.






